Regenerative Therapies

What is Regenerative Therapy?
Medicine has come a long way in the last few decades. With numerous advances in cellular technology, physicians and medical providers have many treatment options available to help enhance their patients’ quality of life. There is a time and a place for conventional medical practices to repair injuries and manage health conditions. However, there are more advanced treatment options available now that can help patients avoid complicated procedures and feel better faster.
Regenerative Therapy uses the body’s own healing mechanisms to repair and regrow at the cellular level. This can help joints heal from an injury, reduce inflammation, and fight apoptosis (cell death). Regenerative Therapy is a collection of safe and effective treatments for patients of all abilities to help heal and repair joints naturally.


The Benefits of Regenerative Therapies
The goal of Regenerative Therapy is to heal the underlying cause of joint discomfort by bringing new life to the damaged tissues in the body. This helps avoid surgery while relieving symptoms and improving quality of life.
For example, knee pain caused by arthritis or an injury is one of the most common orthopedic conditions that individuals seek interventions to resolve. Knee replacement surgery is an expensive, painful procedure requiring 3-6 months of recovery and rehabilitation, with no guaranteed success. However, with one injection and one booster of Platelet-Rich Plasma, patients can experience a significant reduction in pain, improved mobility, and little if no downtime.
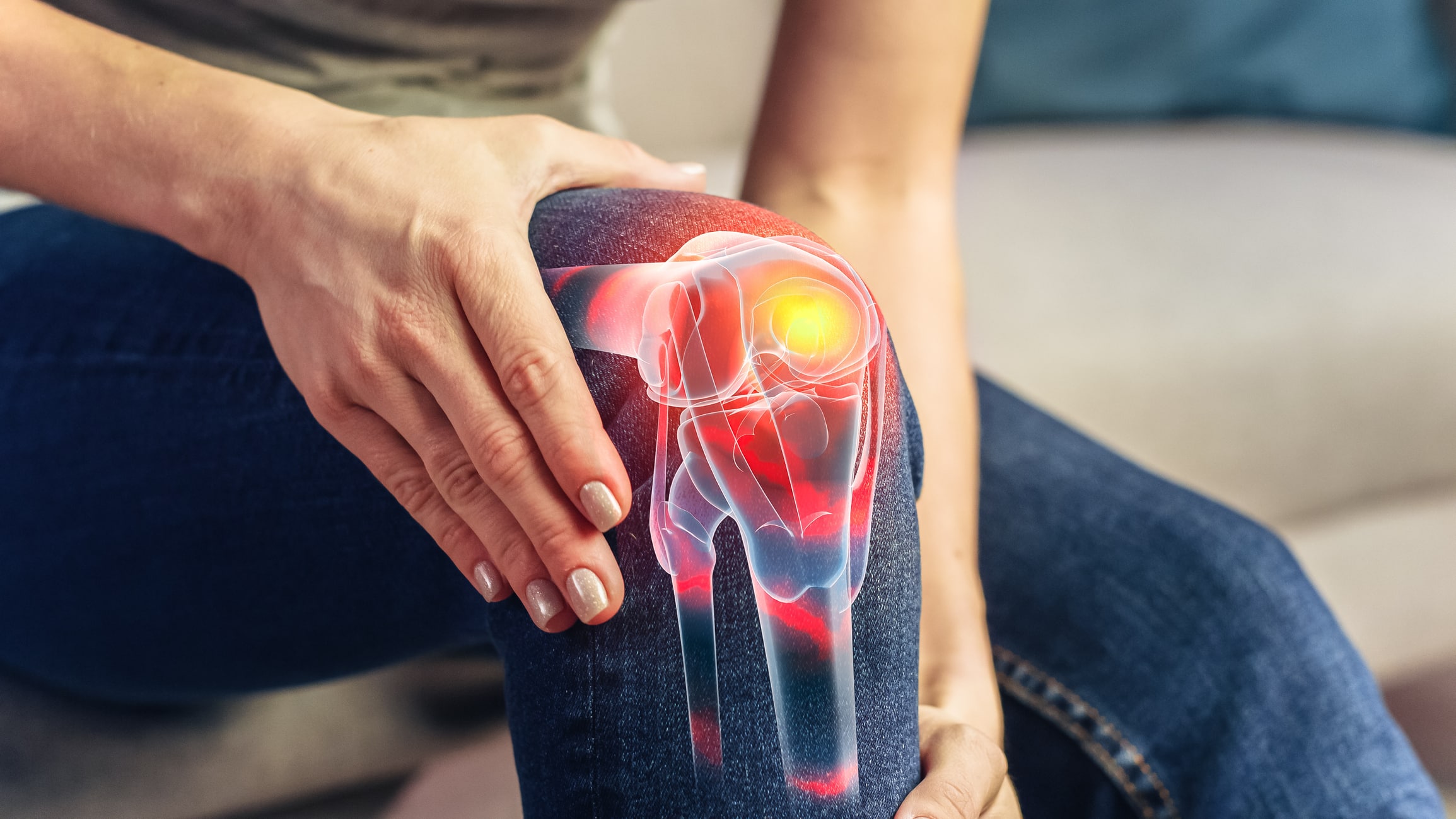
Types of Regenerative Therapies
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma is blood that has been concentrated with platelets via centrifuge. Platelets play an important role in cell reproduction and tissue regeneration that can help stimulate healing. Plasma imitates the blood supply for platelets, allowing platelets to sense the injury and release growth factors. This process helps the body to signal the deployment of new cell growth in an injured area.
PRP Therapy can be used to treat a host of musculoskeletal injuries, specifically joint injuries or pain due to degenerative conditions. It can also be effective in hair restoration and facial rejuvenation by improving fine lines and wrinkles as a result of stimulating and increasing collagen.
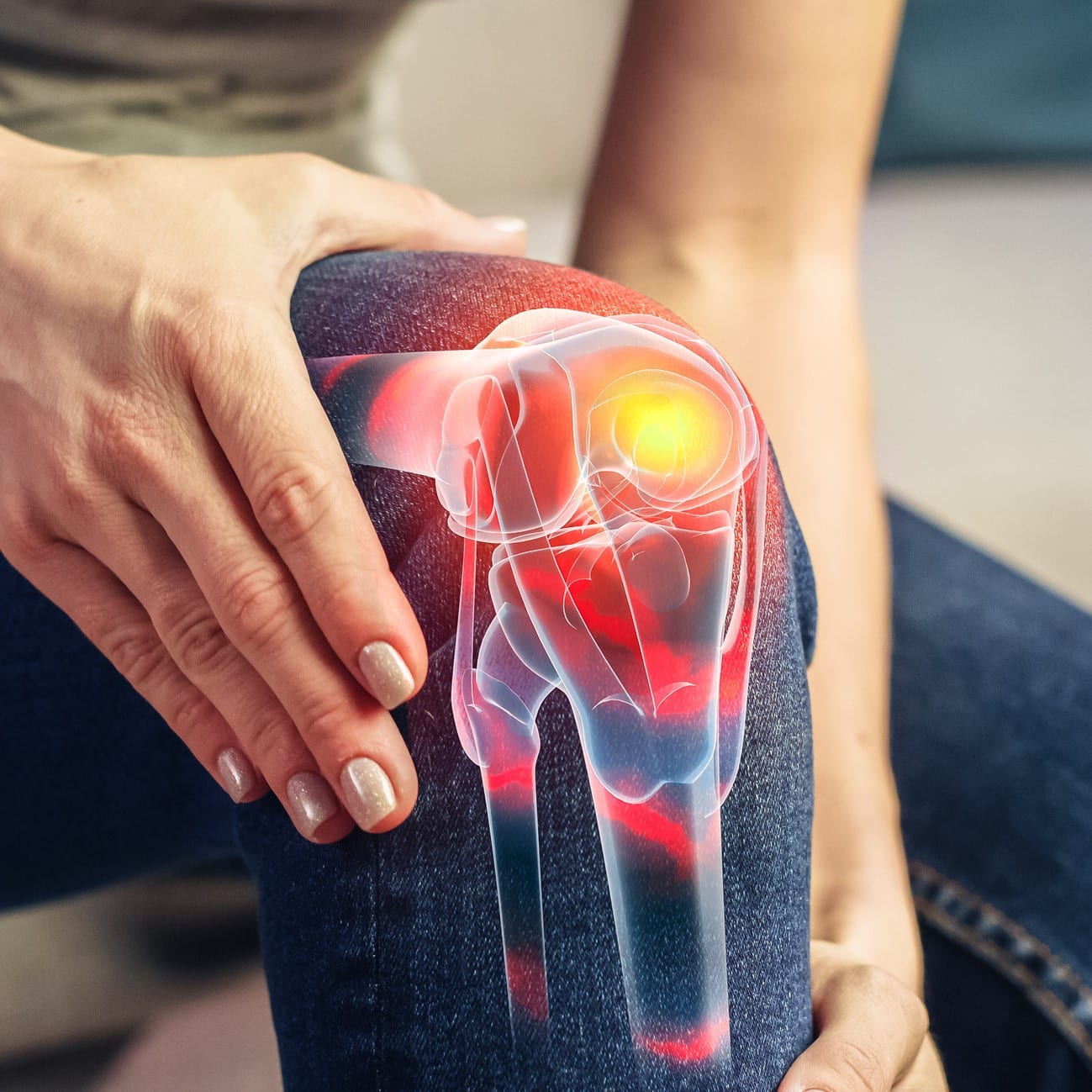
Adipose-Derived Regenerative Therapy
Autologous Nanoparticle Therapy is an advanced regenerative therapy that helps form new tissue, including cartilage, muscle, tendons, and adipocytes.
Cells are the building blocks of life, but they age over time. The body’s concentration of stem cells decreases with age, and existing cells age along with you. Younger cells have a greater ability to multiply and regenerate, whereas older cells lose their ability to multiply. This causes natural-occurring tissue repair to reduce substantially over time. Areas of hypoxia or low oxygen result if there is an inadequate blood supply around the injured area. In addition to blood loss, this can also occur when there is an injury to the joints, tendons, or meniscus tissue. Oxygen-deprived areas may not heal by themselves because they are lacking in repair cells.
Adipose-derived stem cells are a subset of mesenchymal stem cells that are harvested from adipose (fat) tissue. This type of stem cell is 500-1,000 times greater in number in the body than bone marrow-derived stem cells and is “younger” in age which makes them ideal for self-healing.
These stem cells have a vast capability of differentiation that can help repair different types of tissues in the body, providing therapeutic solutions. For example, they can secrete growth factors and peptides that can help support wound healing and differentiate into osteoblasts to regenerate bone tissue. They can also help the body naturally recruit native stem cells or white blood cells to encourage self-repair.
Adipose-derived stem cells are the most common source of mesenchymal stem cells used clinically, as they are more easily harvested. They are typically extracted from the abdominal wall, buttock, or above the iliac crest. Once a viable donor site on the body is identified, a harvesting method can be selected. Liposuction, handheld syringe aspiration, or direct excision can be used to extract adipose tissue from a site.
Donor cells can then be collected and banked for future use. If you require regenerative treatments, you can have access to your bank of adipose-derived stem cells. Using stem cells with your own DNA eliminates the risk of your body rejecting cells or the transmission of infectious diseases when handled by a trusted cell banking company. Learn more about stem cell banking here.
Umbilical cord-derived stem cells can also offer advanced avenues of treatment. The umbilical cord and placenta contain stem cells that can develop into many different cells. The regenerative properties of umbilical stem cells can provide added healing power for a wide variety of orthopedic uses and implications. The major advantages of umbilical cord stem cell therapy are that cells do not have to be exactly matched to the patient from the donor and they can replicate faster than other types of stem cells.
DISCLAIMER – SOME OF THE THERAPIES IDENTIFIED BELOW MAY NOT BE AVAILABLE TO CUSTOMERS BUT ARE PROVIDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES.
For more information or an appointment:
